Como es el sistema circulatorio de un caballos
En el artículo de hoy os contamos a cerca de una de las partes fundamentales para cualquier ser vivo: el…

En el artículo de hoy os contamos a cerca de una de las partes fundamentales para cualquier ser vivo: el…
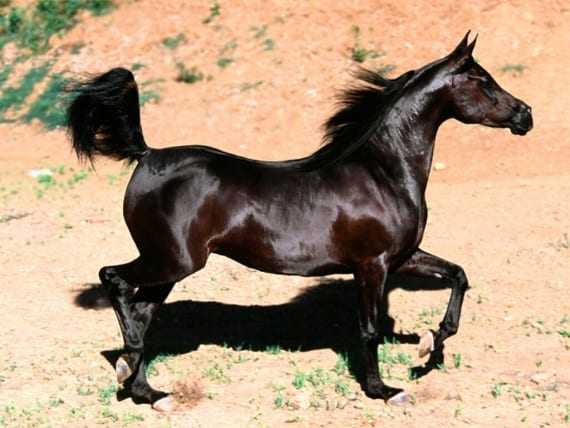

Como consecuencia de la evolución la estructura ósea de los caballos se ha producido algunos cambios. Estos cambios se ven…
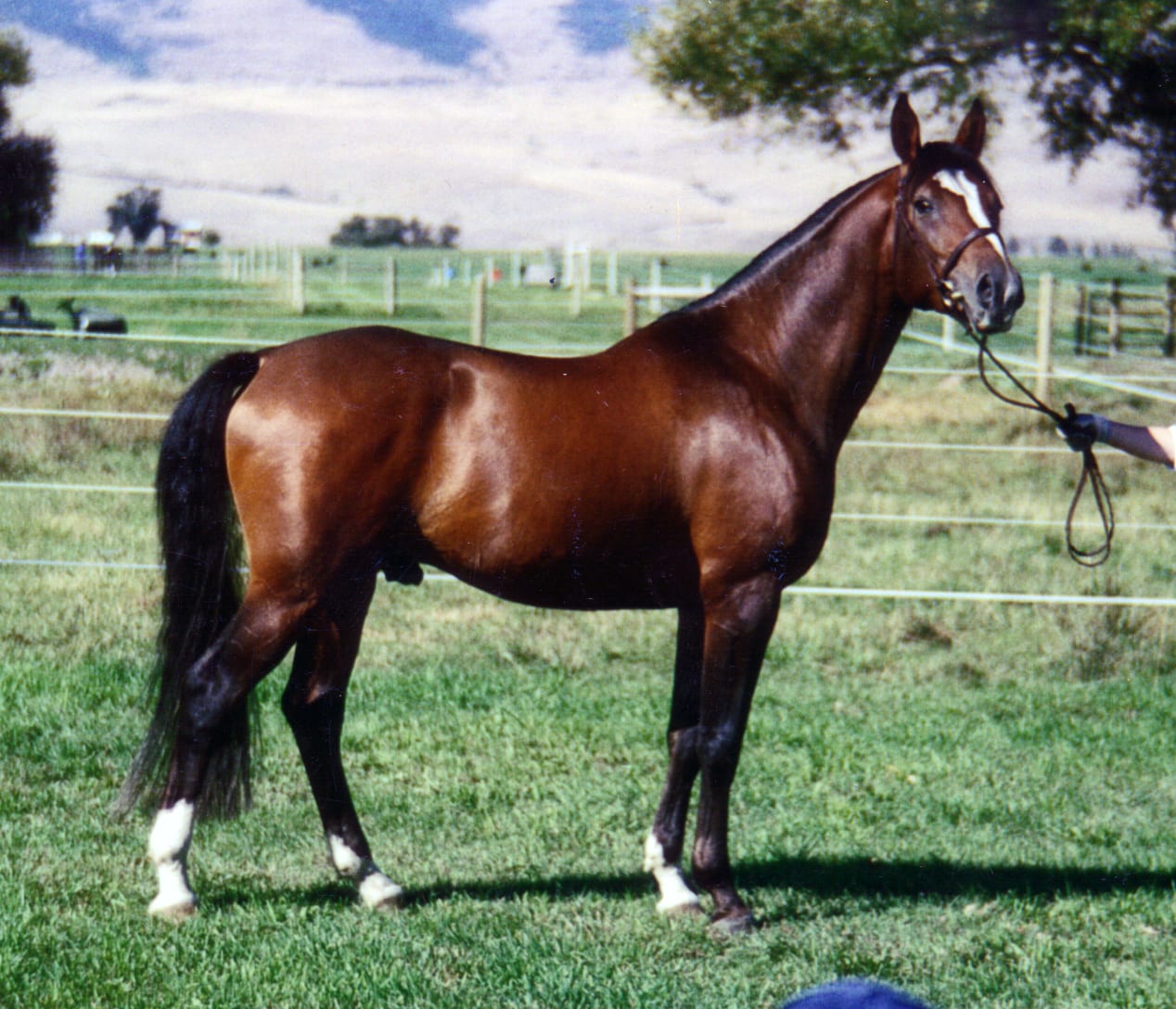

Cuando hablamos de las mejores razas equinas, sin duda el árabe suele estar entre las predilectas de los entendidos en…
En el artículo de hoy vamos a hablar del término “jamelgo”. A lo largo de varios artículos hemos ido aclarando…
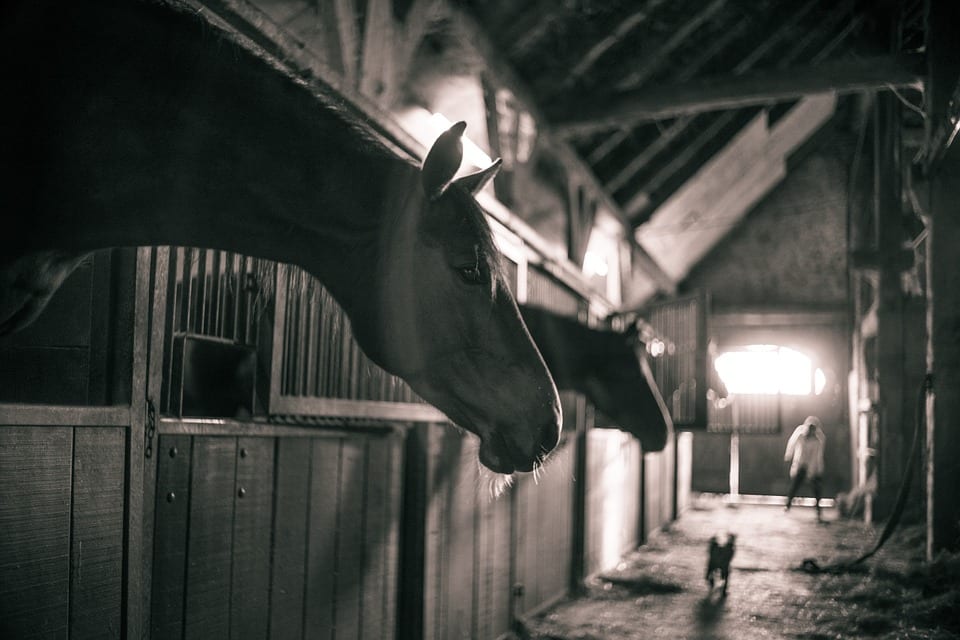

La conocida como la «Yeguada Militar» comienza en España después de los cambios sociales y económicos producidos por la Guerra…
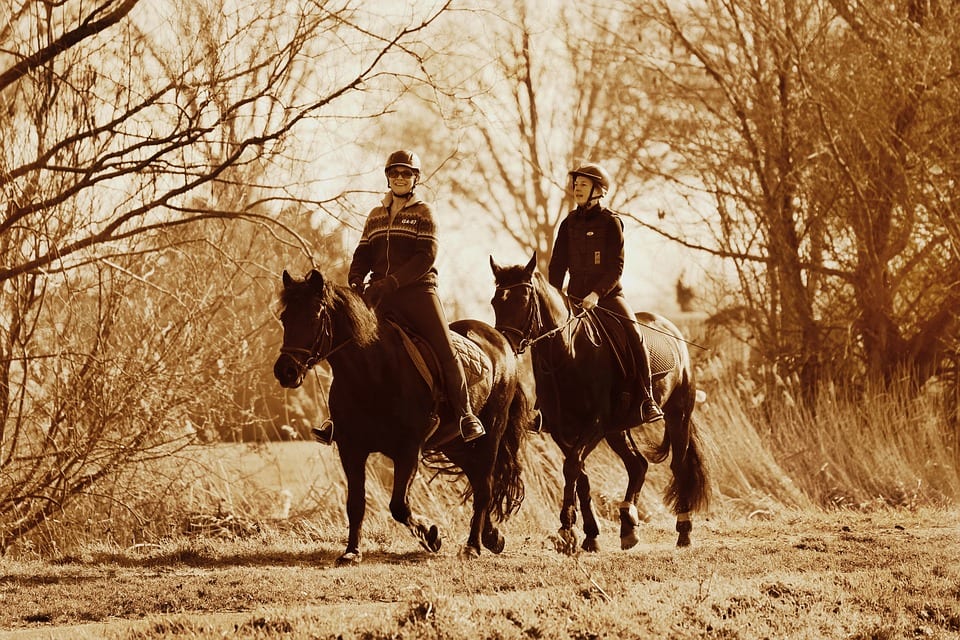

En el artículo de hoy vamos a hablar sobre la Real Federación Hípica Española, su origen y las disciplinas y…
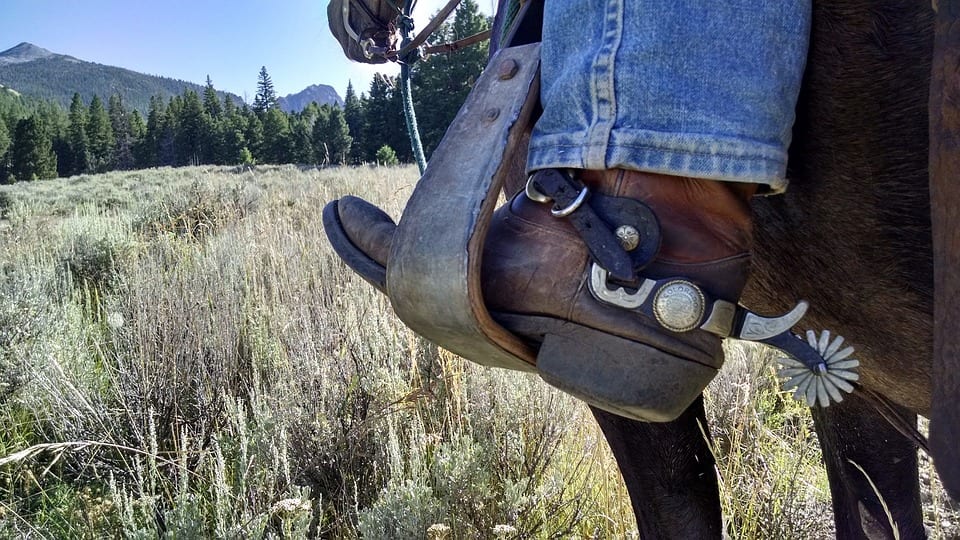

Las espuelas son una herramienta que se pueden utilizar en prácticamente todas las disciplinas ecuestres. Son una especie de espiga…

Los caballitos de juguete ha sido, con el paso de las épocas, uno de los juguetes clásicos. Son muchos los hogares…
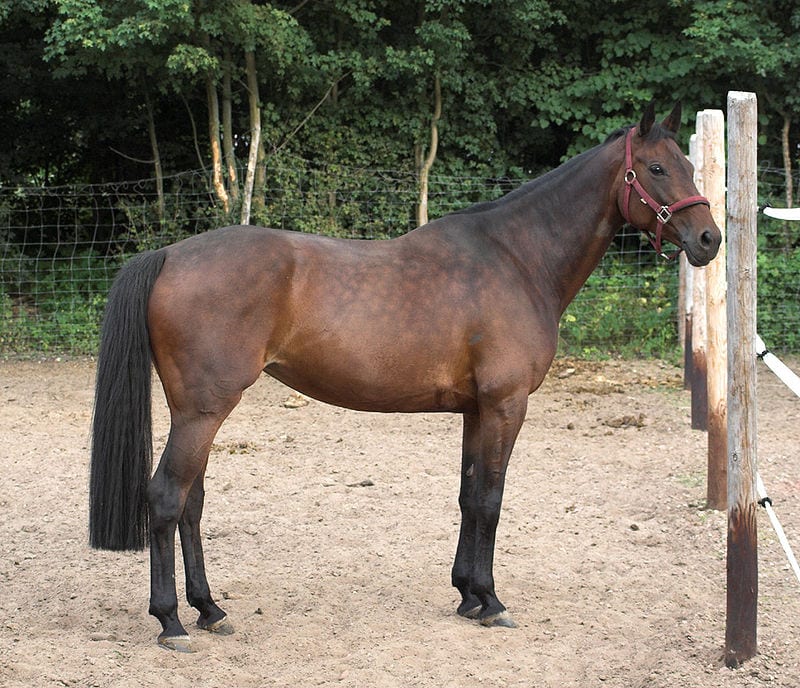

Los Caballos Oldenburg, también conocidos como Oldenburgo, son equinos de sangre caliente procedentes del noroeste de la Baja Sajonia, antiguamente…
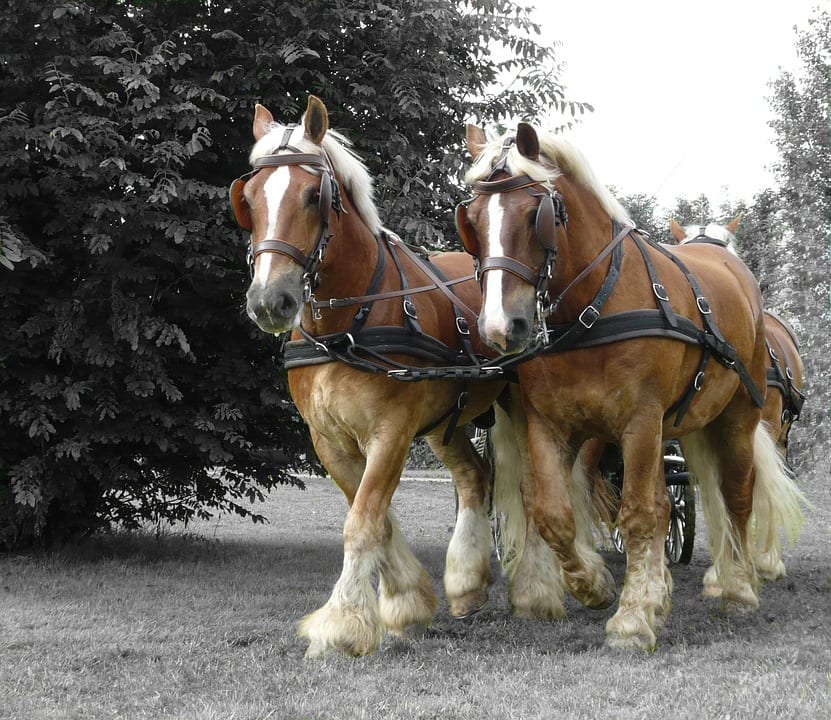

Los caballos de tiro son aquellos utilizados para el trabajo debido a su gran capacidad de tracción. Tradicionalmente se han…
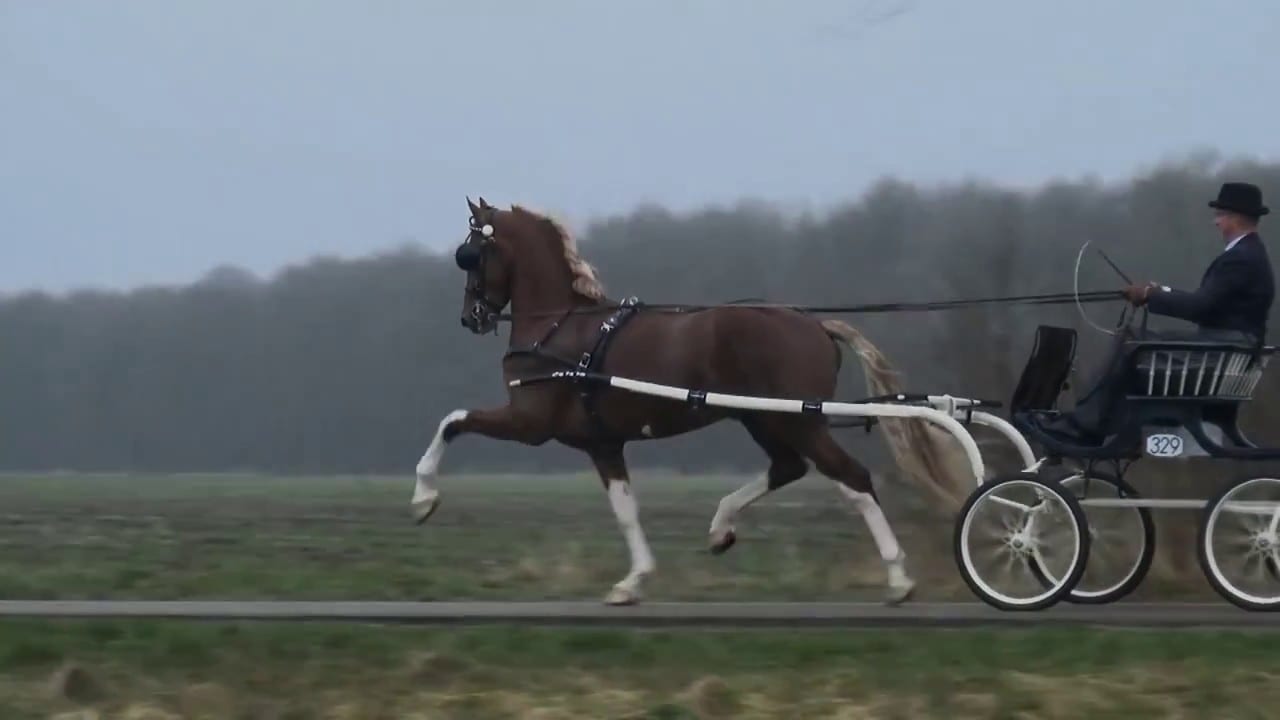

La raza de caballos Hackney, también denominada Norflok Trotter, es de origen británica y es muy apreciada por su gran…